o que e provera
<img class="aligncenter" src="https://scx1.b-cdn.net/csz/news/800a/2023/final-state-emergencie.jpg"
alt="Final state emergencies winding down 3 years into pandemic"
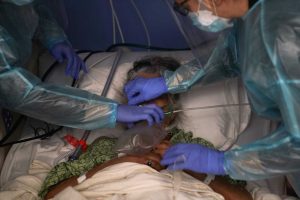
title="Two nurses put a ventilator on a patient in a COVID-19 unit at St. Joseph Hospital in Orange, Calif. Thursday, celexa side effects after 3 days Jan. 7, 2021. California’s COVID-19 emergency declaration ends on Tuesday, Feb. 28, 2023. Gov. Gavin Newsom first issued the emergency declaration on March 4, 2020. The emergency ends just as California officially passed 100,000 COVID-related deaths during the pandemic. Credit: AP Photo/Jae C. Hong, File” width=”800″ height=”530″>
California’s coronavirus emergency officially ends Tuesday, nearly three years after Gov. Gavin Newsom issued the nation’s first statewide stay-at-home order and just days after the state reached the grim milestone of 100,000 deaths related to the virus.
As California’s emergency winds down, such declarations continue in just five other states—including Texas and Illinois—signaling an end to the expanded legal powers of governors to suspend laws in response to the once mysterious disease. President Joe Biden announced last month the federal government will end its own version May 11.
The end of California’s order will have little to no effect on most people as Newsom has already lifted most of the state’s restrictions, like those that required masks, closed beaches and forced many businesses to close. It offers a symbolic marker of the end of a period that once drastically altered the lives of the state’s nearly 40 million residents.
Illinois’ order will end in May alongside the federal order, while the governors of Rhode Island and Delaware recently extended their coronavirus emergency declarations. In New Mexico, public health officials are weighing whether to extend a COVID-19 health emergency beyond its Friday expiration date.
Texas, meanwhile, hasn’t had any major coronavirus restrictions for years, but Republican Gov. Greg Abbott keeps extending his state’s emergency declaration because it gives him the power to stop some of the states’ more liberal cities from imposing their own restrictions, like requiring masks or vaccines. Abbott has said he’ll keep the emergency order—and his expanded powers—in place until the Republican-controlled Texas Legislature passes a law to prevent local governments from imposing virus restrictions on their own.
The conflicting styles show that, while the emergencies may be ending, the political divide is not—foreshadowing years of competing narratives of the pandemic from two potential presidential candidates in Newsom and Abbott.
Newsom has used his authority to make sure all of California’s local governments had restrictions in place during the pandemic, even threatening to cut funding to some cities that refused to enforce them. While California’s emergency declaration is ending, other local emergencies will remain in place—including in Los Angeles County, home to nearly 10 million people.
The Los Angeles emergency order encourages mask use in some public places like business and trains and for residents who have been exposed to the virus. It will remain in effect for at least another month. Tuesday, the Los Angeles County Board of Supervisors will debate whether to end the order March 31.
Many public health experts say it makes sense that California’s order is coming to a close.

“Three years ago, if you … got infected you were rolling the dice about dying,” said Brad Pollock, chair of the Department of Public Health Sciences at the University of California, Davis. “What’s happened in the three years now is we have vaccines, we have antiviral therapy, we have much more knowledge about how we take care of patients in terms of supportive care. Your risk of dying is a fraction of what it was.”
The Newsom administration’s approach was to issue broad restrictions on what people could do and where they could go. California ended up faring better than other states, but they did worse than some other countries, like Sweden, said Jeffrey Klausner, professor of clinical population and public health sciences at the Keck School of Medicine at the University of Southern California.
“I think if we had better focused our resources on those most at risk, we probably could have avoided more deaths,” he said.
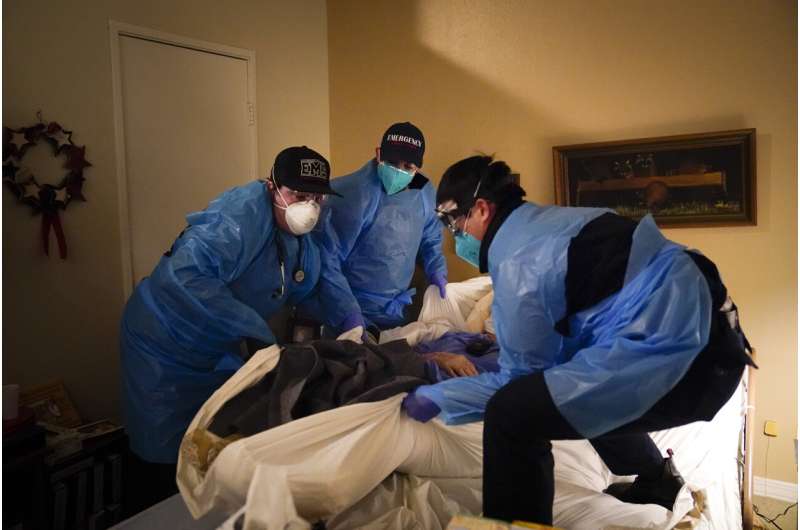
The pandemic strained California’s health care system, which has yet to fully recover, said Carmela Coyle, president and CEO of the California Hospital Association. She said hospitals remain overwhelmed—not from COVID patients, but from an influx of people returning to the health care system after staying away during the pandemic. She said a majority of California’s hospitals are losing money, prompting fears some could close—just as a community hospital in the state’s Central Valley did in December.
-
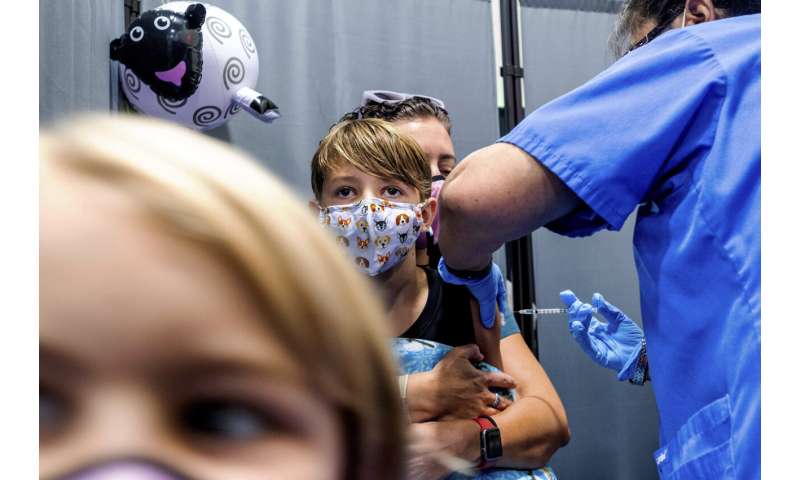
Finn Washburn, 9, receives an injection of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in San Jose, Calif., on Nov. 3, 2021, as his sister, Piper Washburn, 6, waits her turn. California’s COVID-19 emergency declaration ends on Tuesday, Feb. 28, 2023. Public health experts say the pandemic has not ended, but the virus is much more manageable with the availability of vaccines and other treatments. Credit: AP Photo/Noah Berger, File
-

Gov. Gavin Newsom announces the next phase of California’s COVID-19 response called "SMARTER," during a press conference in Fontana, Calif. on Feb. 17, 2022. California’s COVID-19 emergency declaration ends on Tuesday, Feb. 28, 2023. Gov. Newsom first issued the emergency declaration on March 4, 2020. Credit: Watchara Phomicinda/The Orange County Register via AP, File
“While the state’s COVID public health emergency is formally concluding, the health care system emergency remains,” Coyle said.
Health care workers have felt the strain, too, working long hours among people infected with a highly contagious and potentially life-threatening disease. The strain has prompted a workforce shortage, with competing proposals to remedy it. The California Hospital Association is asking for a one-time infusion of $1.5 billion to help keep hospitals afloat. Labor unions, meanwhile, are backing a bill that would impose a $25 minimum wage for health care workers.
Meanwhile, local public health departments worry the end of the coronavirus emergency will mean a return to limited funding for their budgets, an issue exposed in the early days of the pandemic when many counties did not have enough people to respond to the crisis. Newsom signed a budget last year that will spend $200 million to help public health departments hire more workers. This year, he’s proposing cutting nearly $50 million in public health workforce training programs, part of his plan to cover a projected budget deficit.
“Public health is dependent on their frontline workforce, and that frontline workforce has to be skilled and trained and educated,” said Michelle Gibbons, president of the County Health Executives Association of California.
Overall, Newsom’s budget proposal would sustain $300 million in public health spending, including $100 million for 404 new positions in the state Department of Public Health, including areas of workforce training and emergency preparedness and response. The money will “modernize state and local public health infrastructure and transition to a resilient public health system,” said H.D. Palmer, spokesperson for the California Department of Finance.
© 2023 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.
Source: Read Full Article