Home » Health News » Page 14

Reviewed To age or not to age! How does aging affect organisms on a cellular level? What mechanisms help cells survive self-inflicted or external harm? It is known that lysosomes-;critically important cellular structures-;are crucial for digesting damaged cellular components and pathogens, and maintain stability within cells and tissues. But can they also be repaired, and if so, how? In a […]
» Read more
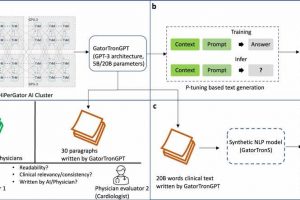
A new artificial intelligence computer program created by researchers at the University of Florida and NVIDIA can generate doctors’ notes so well that two physicians couldn’t tell the difference, according to an early study from both groups. In this proof-of-concept study, physicians reviewed patient notes—some written by actual medical doctors while others were created by the new AI program—and the […]
» Read more
Reviewed Soccer fans exhibit different patterns of brain activation while watching a match that may trigger positive and negative emotions and behaviors, according to research being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The researchers say the implication of these findings could extend beyond sports to fanaticism in other areas, such as […]
» Read more

A recent study delves into the behavioral complexities of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by introducing the rigid-autonomous phase sequence (RAPS) formation concept. RAPS may be responsible for the cognitive, sensory-motor, and memory-related challenges faced by individuals with ASD. By uniting these insights under a single theoretical framework, this research paves the way for innovative treatments, promising a brighter future for […]
» Read more
Reviewed More than 1,100 experts have joined the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine in boycotting the medical journal Nutrients until it stops publishing egregious animal experiments that could have been ethically conducted in humans. The boycott, which also applies to Nutrients' publisher, MDPI, comes after repeated requests to the journal's editors asking them to institute sound editorial practices. A letter […]
» Read more

Around one in five American adults manage to squeeze in watching a movie on a daily basis. It’s a great way to escape the daily grind and unwind with loved ones. But, what can you actually remember about last night’s film? You may be able to remember the title, the rough story outline or the Hollywood star who acted in […]
» Read more
A recent publication from Audrey Gérard’s lab looks at how a specific protein, called IFNγ, can coordinate CD8+ T cell responses during a flu infection. CD8+ T cells are a type of white blood cell responsible for recognizing and destroying cells that have been infected with viruses, as well as some types of cancer. They are controlled by a complex […]
» Read more

Neuromelanin-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging (NM-MRI) contrast is associated with psychosis severity in antipsychotic-free patients with schizophrenia, according to a study published online Nov. 8 in JAMA Psychiatry. Kenneth Wengler, Ph.D., from Columbia University in New York City, and colleagues conducted a cross-sectional study involving 42 antipsychotic-free patients with schizophrenia, 53 antipsychotic-free individuals at clinical high risk for psychosis (CHR), and […]
» Read more

BBC Breakfast: Claire Hopkins discusses loss of smell Around two million people in the UK are thought to be living with long Covid, an exhausting condition that can make everyday life difficult. It is defined as symptoms that start within three months of a Covid infection and linger for at least two months. These symptoms can include fatigue, brain fog, […]
» Read more
Reviewed Associative learning was always thought to be regulated by the cortex of the cerebellum, often referred to as the "little brain". However, new research from a collaboration between the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, Erasmus MC, and Champalimaud Center for the Unknown reveals that actually the nuclei of the cerebellum make a surprising contribution to this learning process. If a […]
» Read more









