Home » Health News » Page 149
A University of Central Florida College of Medicine researcher has developed a new, more precise treatment for a major cause of illness around the world each year—acute respiratory viral infections. Acute respiratory viral infections include sicknesses such as the flu, pneumonia, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and coronavirus. These infections cause millions of illnesses worldwide, with the flu alone responsible for […]
» Read more
SEATTLE ― The use of Mohs surgery may improve survival for patients with early-stage Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC), results from a large, retrospective study show. As compared with conventional wide local excision, survival was significantly improved among patients treated with Mohs, and a subgroup analysis showed that the survival benefit remained for patients with risk factors. “At 10 years, overall […]
» Read more
Source: Read Full Article
» Read more
As the executor of life activities, proteins exert their specific biological functions through interactions such as forming protein complexes. The localization effects, crowding effects, and organelle microenvironments within cells are crucial for maintaining the structure and function of protein complexes. Recently, a research team led by Prof. Zhang Lihua from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese […]
» Read more

Angelina Jolie shared a vital reminder on Monday (May 8) in honor of World Ovarian Cancer Day, and what would have been her late mother’s 73rd birthday. Related story Angelina Jolie’s Son Maddox Jolie-Pitt Looks All Grown Up in This Super-Rare Outing to the White House In an emotional Instagram post, the Oscar-winning actress opened up about losing her mother […]
» Read more

Findings Due to a policy decision in 2010 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the price of a prescription for the therapeutic gout drug colchicine increased nearly 16-fold from $11.25 in 2009 to $190.49 in 2011. Out-of-pocket costs for patients who took the drug jumped more than four-fold from $7.37 to $39.49 over the same period. Use of […]
» Read more

When the summer heat settles in, your favorite rich and chocolatey desserts hit a little too hard. You need something light, airy, and fruity to end your summertime meals on a high note, and Nancy Fuller’s Strawberry Jelly Roll is all of the above. It’s a fluffy, moist cake lined with sweet and tart strawberry jam, rolled up neatly, and […]
» Read more
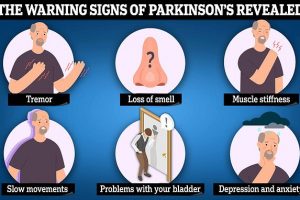
Parkinson’s might be caused by common bug found in the gut, researchers say Researchers in Finland suggest bacteria Desulfovibrio is a cause of Parkinson’s They say the bug cause proteins to clump, resulting in the injury or death or cells READ MORE: Doctors reveal first little-known warning sign of Parkinson’s Parkinson’s might be caused by a little-known aquatic bacteria, researchers have said. […]
» Read more

Asian Americans have significant differences in genetics, socioeconomic factors, culture, diet, lifestyle, health interventions and acculturation levels based on the Asian region of their ancestry that likely have unique effects on their risk for heart disease and Type 2 diabetes, according to a new American Heart Association scientific statement published today in the Association's flagship, peer-reviewed journal Circulation. While often […]
» Read more

If you’re a health care provider treating people with type 2 diabetes (T2D), University at Buffalo researcher Mehmet A. Eskan has this suggestion for you: check your patients’ teeth. In a study published in PLOS ONE on April 14, Eskan demonstrates that patients with T2D who have full chewing function have a blood glucose level that is significantly lower than […]
» Read more









