Researchers decipher a new way that immune cells detect infections and cancers

Published today in Science, the research team from the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute), the Olivia Newton-John Cancer Research Institute and CSL Limited say this breakthrough of discovering how gamma-delta T cells become activated addresses a question that has baffled scientists for 25 years.
The study by University of Melbourne’s Marc Rigau, Ph.D. student at the Doherty Institute, was co-led by Dr. Adam Uldrich, a Senior Research Fellow at the Doherty Institute, Professor Dale Godfrey a laboratory head at the Doherty Institute, and Dr. Andreas Behren, a Laboratory Head from the Olivia Newton-John Cancer Research Institute.
Dr. Uldrich explained that gamma-delta T cells are known to respond to the presence of small molecules, known as phosphoantigens, that are produced by bacteria and cancer cells.
“This leads to the activation of these gamma-delta T cells and often eradication of the diseased cells.”
Professor Godfrey said “Up until now, scientists have struggled to understand the fundamental question of how phosphoantigens are detected by gamma-delta T cells.”
“We found that molecules on the surface of the gamma-delta T cells, called T cell receptors, bind to another molecule called butyrophilin 2A1 that is present on many different cell types throughout the body, including cancer cells.”1
Dr. Behren said “These findings represent a key advance in our understanding of how gamma-delta T cells function to protect us from disease.”
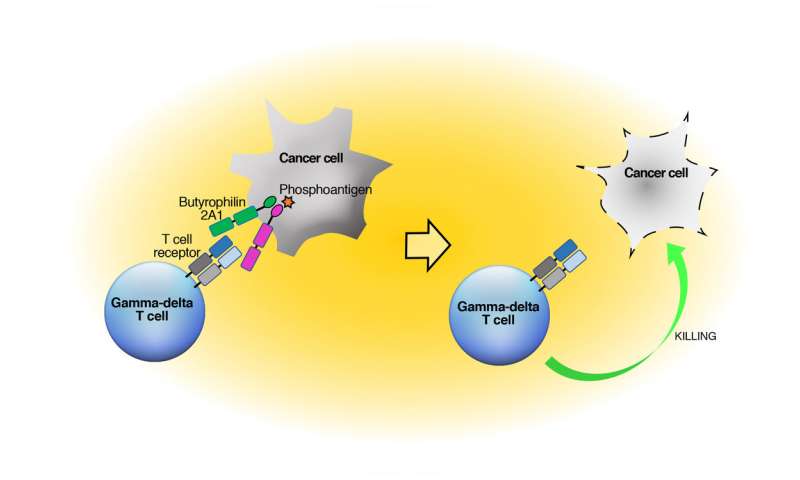
“The research team believes that this breakthrough could ultimately lead to the development of new and improved immunotherapy treatments for millions of people worldwide impacted by cancer and infection.”
The research is the result of a collaboration between the Doherty Institute, the Olivia Newton-John Cancer Research Institute, and CSL Limited.
“This research project demonstrates the power of collaboration between academia and industry. Nearly a decade ago, we identified Butyrophilin 2A1 as a potential therapeutic target but its precise biological function remained elusive,” said Dr. Con Panousis, Senior Director Molecular Biology, CSL Limited and an author on the paper.
“This discovery makes a significant contribution to our understanding of how gamma-delta T cells work and in doing so, paves the way for translating this research into new immunotherapies for the treatment of serious human disease.”
Source: Read Full Article