Study of interleukin-6 impact on organoids shows increase in radial glia cells
A team of medical researchers at the University of Tübingen’s Hertie Institute for Clinical Brain Research in Germany has found that exposing organoids at a certain stage of growth to interleukin-6 leads to an increase in radial glia cells, which may provide a hint as to why pregnant women who experience infections are more likely to deliver a child who develops autism.
In their study, reported in the journal Molecular Psychiatry, the group tested the impact of maternal infections on the brain of a growing fetus using organoids as a stand-in.
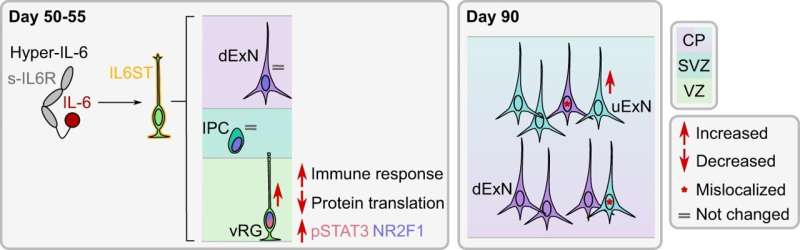
To learn more about the possible impact on the brain of a developing fetus caused by a pregnant woman fighting off an infection, the research team grew brain organoids using stem cells—they were meant to mimic the growing fetus brain. Next, to test the impact of a mother fighting off an infection, they exposed the organoid to hyper-IL-6, a molecule produced by white blood cells when the body is fighting off an infection. Prior research has shown that it can lead to inflammation and influence brain development in fetal mice. The exposure lasted from five to 10 days to simulate an infection period and was done when the organoid was 45 days old to mimic neocortex development during early gestation.
Tissue taken from the organoid after the exposure exhibited increased levels of radial glia cells. The researchers also found an associated change in gene expression related to the glia cells. And they found abnormal changes in upper-layer neuron development 35 days after treatment. The team was also surprised to see differences in gene expression in the organoids that had not been observed in mouse models treated in similar ways, suggesting that the impact of an immune response in pregnant mice may be different than for humans.
The findings add to evidence of an association between the development of autism and abnormal neuroprogenitor differentiation. The researchers plan to conduct similar studies adding new factors, such as microglia, to more closely mimic the impact of an immune response on a growing fetus.
More information:
Kseniia Sarieva et al, Human brain organoid model of maternal immune activation identifies radial glia cells as selectively vulnerable, Molecular Psychiatry (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41380-023-01997-1
Journal information:
Molecular Psychiatry
Source: Read Full Article