Study suggests SARS-CoV-2 virus enters the brain by using cells in the nose to make nanotube tunnels
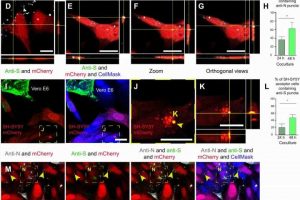
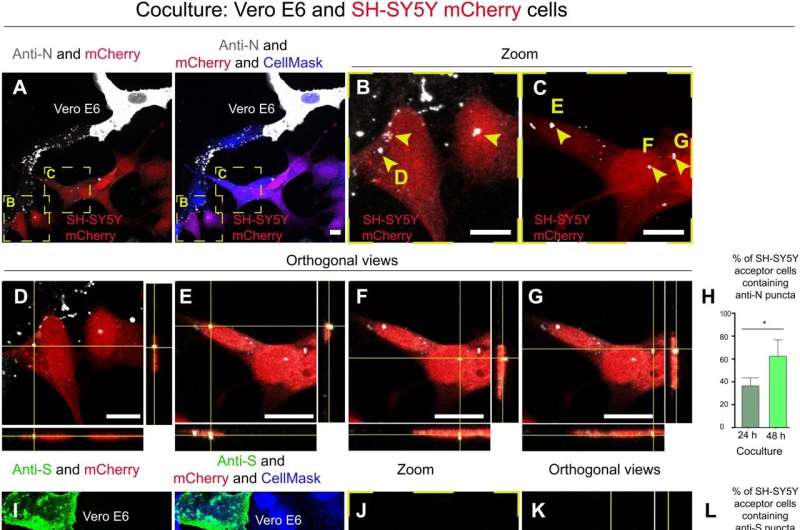
A team of researchers at Institut Pasteur reports evidence that suggests the SARS-CoV-2 virus is able to enter the brain by using nose cells to make nanotube tunnels. In their paper published in the journal Science Advances, the group describes their study of the virus behavior when infecting certain types of cells and using high-powered microscopes to study its movement.
Throughout the course of the pandemic, doctors and patients have been reporting symptoms of confusion and brain fog, suggesting that the SARS-CoV-2 virus is able to enter and infect the brain. But until now, there was little evidence of how it was doing so. Prior research showed that in nerve cells, the virus was not able to use the ACE2 receptor that underlies nose, mouth and other cell infections, making it difficult to understand how it could reach the brain. In this new effort, the researchers believe they may have found the answer—the virus builds nanotube tunnels from cells that do have the ACE2 receptors to use as a conduit to the brain.
In their work, the researchers studied the behavior of two kinds of cells in a dish in their lab—SH-SY5Y, which are similar to cells in the brain, and Vero E6, which are similar to cells that line the nose and other surfaces that are easily infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus. They found that the virus had a difficult time infecting the SH-SY5Y cells, but were able to make their way to the brain cells nonetheless. That led the researchers to take a closer look using an electron microscope. They found that the virus was using the Vero E6 cells to create nanotubes. And because they were made from Vero E6 cells, the virus was able to infect its way through the nanotube tunnels all the way to the brain cells due to the presence of the ACE2 receptors.
Source: Read Full Article